ON A MISSION TO
SET POWER FREE
Green is the global power network of the future. Our team of passionate visionaries, developers and engineers work to provide technology for innovative energy solutions.


ON A MISSION TO
SET POWER FREE
Green is the global power network of the future. Our team of passionate visionaries, developers and engineers work to provide technology for innovative energy solutions.
Upgrade a 100-year-old energy grid and change the world for billions.
As of 2024, the world's population reached 8.2 billion people. This is more than three times the population in 1950, when it was estimated to be 2.5 billion. Yet, a staggering 675 million people are still living without electricity, which means limited or no access to technology, education, and healthcare.
Experts define energy poverty as the lack of modern cooking fuels and sufficient lighting - essentially, a recipe for struggle. Without access to electricity, schools can’t harness technology, and health centers can’t deliver the care people need.
Research has shown that access to electricity is a game-changer, significantly boosting income and educational opportunities. Studies reveal that being plugged into the grid can supercharge both earnings and learning. These findings underscore the urgent need to tackle energy poverty - because when it comes to improving quality of life, electricity is the spark that lights the way.
But the current energy infrastructure across the world faces several critical challenges:
Dominance of Utility Monopolies: In many countries, energy markets are dominated by large, state-owned or private utility companies that control the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. This centralization can limit competition and consumer choice, often resulting in higher prices and less innovation
Grid Structure: Many countries have centralized electrical grids that rely on large-scale power plants, often located far from urban centers. These grids are typically managed by a few entities, which can create vulnerabilities to outages and disruptions, especially during extreme weather events or geopolitical tensions.
Fossil Fuel Reliance: A significant portion of global energy production still comes from centralized fossil fuel power plants. This reliance on large, centralized facilities contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, while also making energy systems more susceptible to supply disruptions.
Regulatory Frameworks: Energy sectors are often heavily regulated, with government agencies overseeing the operation of utilities and energy markets. In many cases, these regulations favor established players and large-scale projects, reinforcing centralization.
Emerging Decentralization Trends: There is a growing trend toward decentralization in the energy sector, driven by advancements in renewable energy technologies, energy storage, and smart grid solutions. Distributed energy resources (DERs), such as solar panels, wind turbines, and local energy storage systems, are becoming more prevalent, allowing consumers and communities to generate and manage their own energy.
Regional Variations: The degree of centralization varies widely by region. For example, countries like Germany and Denmark have made significant strides in integrating decentralized renewable energy sources into their grids, while others may still rely heavily on centralized fossil fuel generation.
Challenges to Decentralization: Despite the potential for decentralization, challenges remain, including regulatory barriers, the need for updated infrastructure, and the integration of distributed resources into existing grids. Additionally, many regions still depend on centralized power generation and distribution models.
Every industry, healthcare, telecom, real estate, finance, they all use data to digitize and innovate. But energy never got the memo. The industry is run by analog monopolies that really haven't changed the way they operate for a hundred years. Energy has a massive data problem, and without data, we really can't innovate.
Imagine you own an electric vehicle. How do you know where the energy is coming from?
You need data to actually know when it’s the right time to charge, and whether the energy providing the electricity to that charging station is gonna be clean or not? Where's our power coming from? How much does it cost? Is there different pricing based on what time of day you're charging? When is it the cheapest energy? When is it the cleanest energy?
Only with access to data can energy innovators build the energy technology solutions we need to power the sustainable energy economy of the future.
But here's the problem. That data is impossible to access. It's scattered and siloed across thousands of individual utilities without a single source of truth.
Green is Decentralizing The Global Power Industry.
Green has cracked the code and is doing things no one else has. Green is using blockchain, the technology of bitcoin, to shift away from centralized practices, towards a more distributed and decentralized model involving, independent power producers. The Green blockchain and node network provides the framework for powering disruptive blockchain technology. The Green community is comprised of a diverse global network of independent Green Smart Node owners and operators committed to decentralizing power industry and increasing energy access.
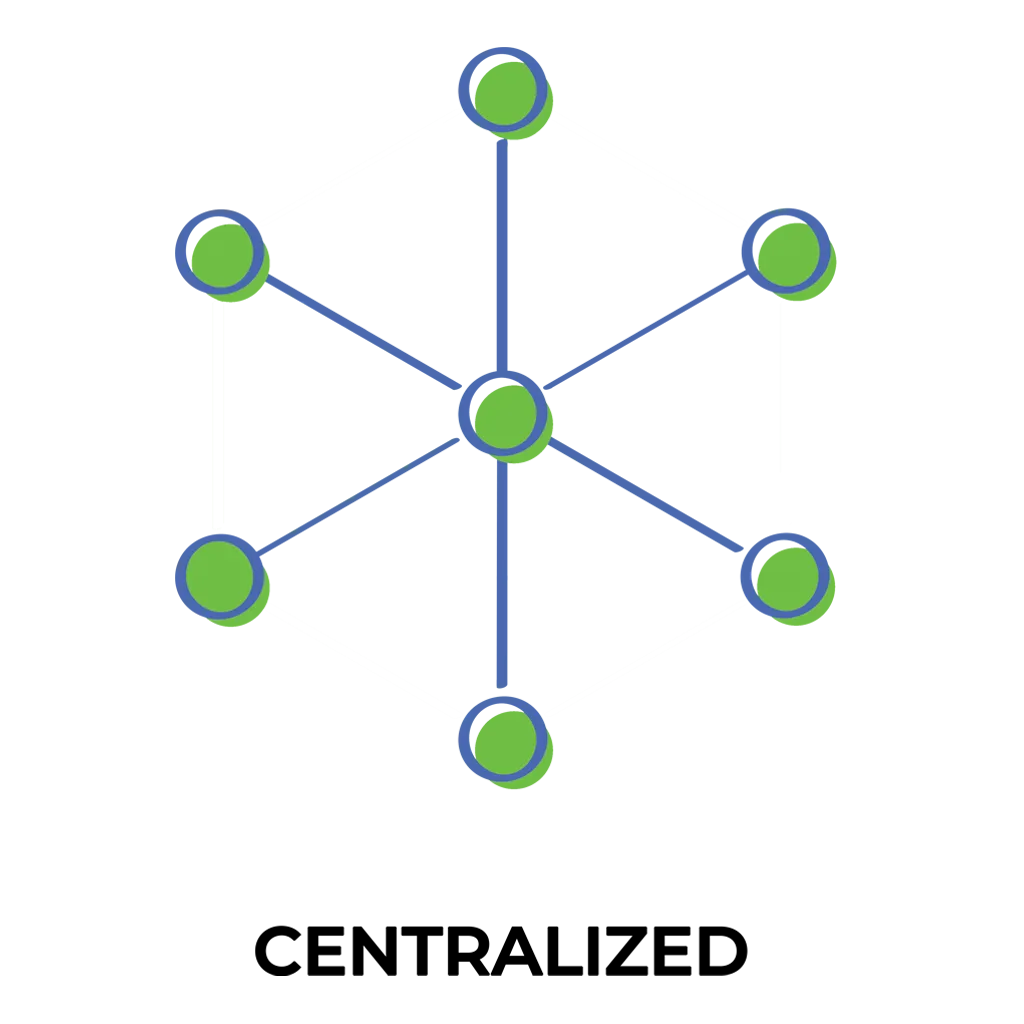
In a centralized model, a small number of large corporations or entities have significant control over the power market, from production to distribution.
Centralized energy models can be misused, leading to higher prices and poor service due to lack of competition. They often prioritize fossil fuels over renewables, causing environmental harm and inefficient resource use. These systems may lack transparency, making it hard for consumers to trust them, and struggle to adapt to changing demands. They can also overlook local needs, increase energy inequality, and be vulnerable to disruptions, while resisting new technologies that could benefit consumers.

A decentralized model consists of a diverse number of independent power producers. Ownership and decision-making are distributed among individuals.
A decentralized energy model features local energy generation from renewable sources, reducing transmission losses and enhancing security. It empowers consumers, to generate, consume, and trade energy. Smart grid technology allows for real-time monitoring and efficient integration of renewables. This model is more resilient to disruptions, offers transparency through blockchain, and promotes sustainability by prioritizing renewables. It also gives communities greater control over their energy resources, enabling tailored solutions and dynamic pricing that encourages responsive energy usage.
The Green Blockchain.
The Green blockchain and token empower partners across the entire ecosystem. By creating radical transparency into the infrastructure and technology of operations, the Green platform offers decentralization, immutability, and transparency, allowing users to verify data authenticity. The system enhances security with cryptography, supports smart contracts for automation, and provides censorship resistance. Additionally, it can lower costs and ensure data redundancy, creating a reliable and user-controlled power model.

Earn.
A new, more efficient way to Support the blockchain and earn green.
Operating Green Smart Node software, typically on a computer, to power the Green blockchain and earn GREEN a digital reward.
Earn.
A new, more efficient way to Support the blockchain and earn green.
Operating Green Smart Node software, typically on a computer, to power the Green blockchain and earn GREEN a digital reward.

Blockchain Mining
Green can facilitate smart blockchain mining.
Smart Energy Grid
Support the expansion of the smart energy grid.
Connected Devices
Install and operate your Green Node using your computer.
Use.
Use GREEN to reduce or completely eliminate your monthly power bill.
While there are a variety of sophisticated use cases for the Green Smart Energy Grid, many users simply reduce or eliminate their monthly power bill by using GREEN.

Use.
Use GREEN to reduce or completely eliminate your monthly power bill.
While there are a variety of sophisticated use cases for the Green Smart Energy Grid, many users simply reduce or eliminate their monthly power bill by using GREEN.

How It Works
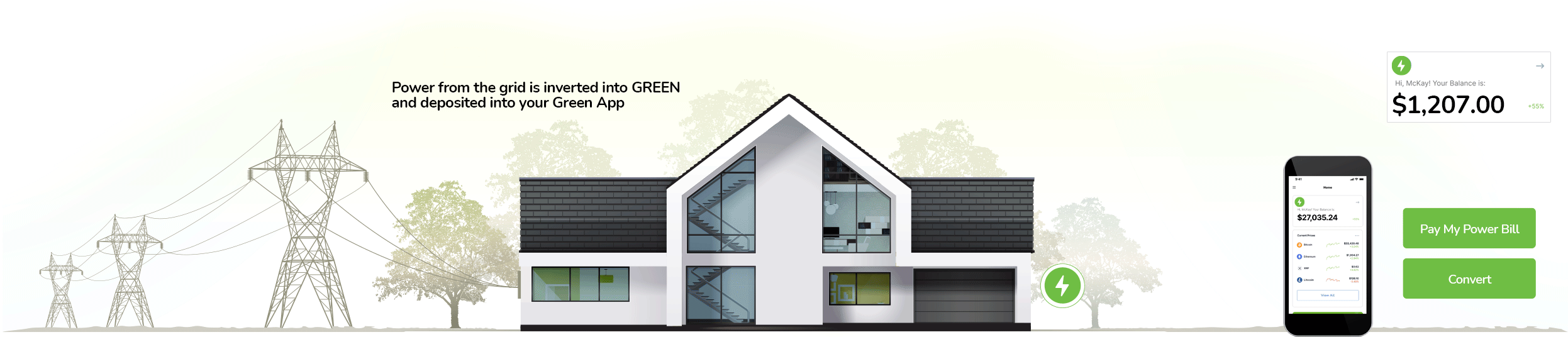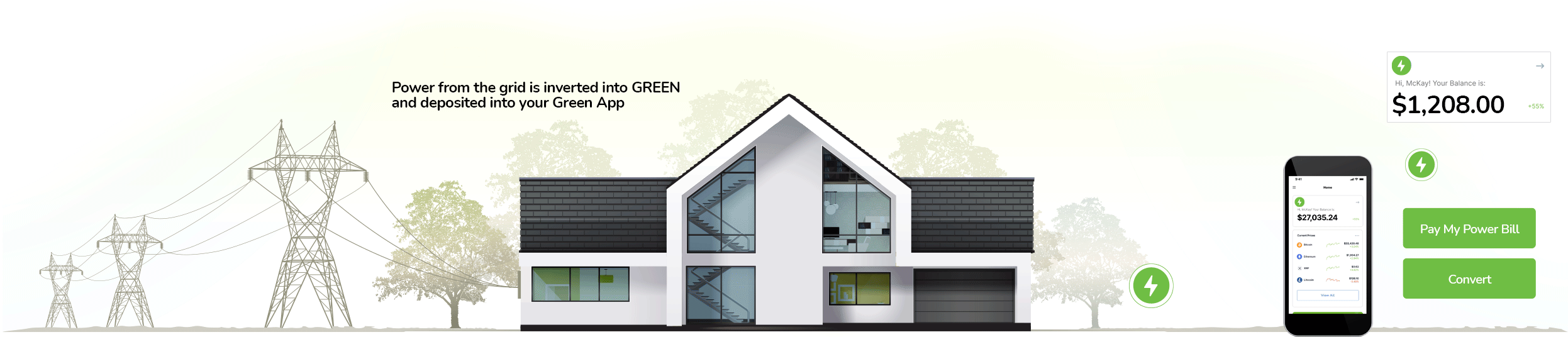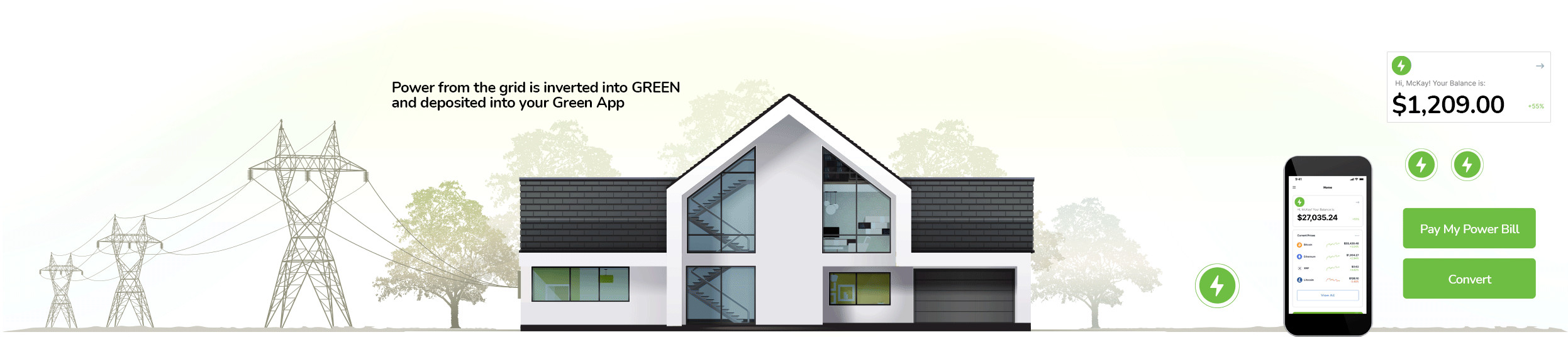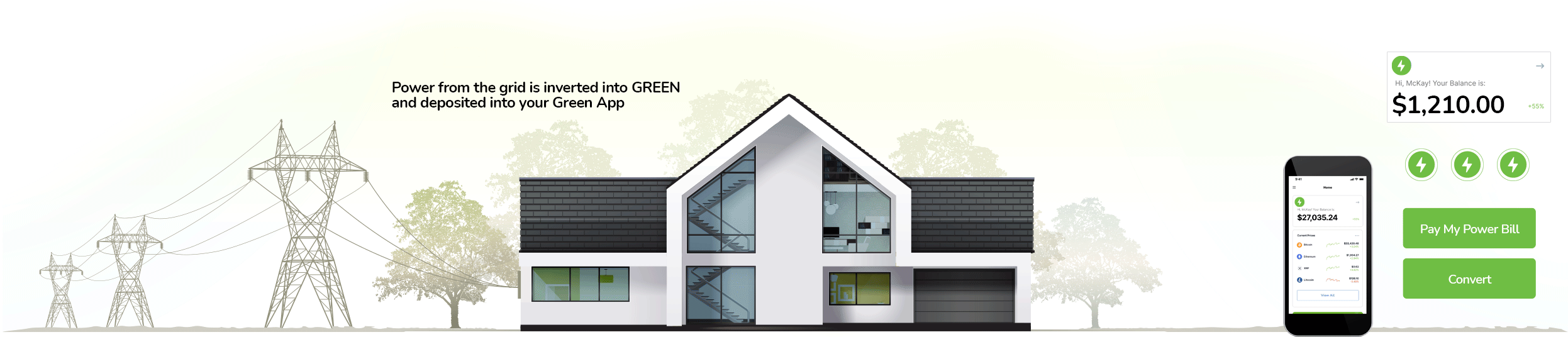
How It Works

More GREEN
Maximize your GREEN Rewards by operating more Smart Node Licenses.
Maximize GREEN
Offset the cost of your solar power system when operating your Smart Nodes.

Share.
Share your power and earn GREEN. Now you can help to power the energy grid of the future.
We are a community dedicated and committed to building the Green Smart Grid. Green Nodes link together to form a smarter, more secure power grid.
Share.
Share your power and earn GREEN. Now you can help to power the energy grid of the future.
We are a community dedicated and committed to building the Green Smart Grid. Green Nodes link together to form a smarter, more secure power grid.

Green Nodes and the Green Blockchain are governed by a Distributed Governance Framework (DGF), which is distinct from and not solely controlled by Green Blockchain (US). Any value derived from Green Nodes and the GREEN Digital Rewards/Tokens is likely to be uncorrelated with the success or failure of Green Blockchain. We do not sell tokens or digital rewards. The Green Blockchain, which is governed by Green Node Owners, self-govern the distribution of GREEN Digital Rewards/Tokens. GREEN Digital Rewards are earned in exchange for work and action on the Green Blockchain. GREEN Digital Rewards are designed to have utility throughout the Green Ecosystem for the purchase of our products and services. The GREEN Digital Reward is not an investment product and may never have any value outside of the Green Ecosystem. Green Node Owners should not expect to recognize any value from the GREEN Digital Reward other than its utility within the Green Ecosystem. We do not anticipate correlation between the GREEN Digital Reward value and our business activities.
PowerPay as described herein remains a work in progress and it may never operate as currently intended. The statements contained herein are aspirational and should not be relied upon, including but not limited to statements relating to Green’s liquidity with the Switch Reward Card. The Switch Reward Card is not affiliated with Green or Green Blockchain and we make no representation that Switch Reward Card will become operational or that it will ever support Green reward.
This document may contain forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties.
Forward-looking statements discuss plans, strategies, prospects, and expectations concerning the business, operations, markets, risks, and other similar matters. There may be events in the future that we cannot accurately predict or control. Any forward-looking statement contained herein speaks only as of the date on which it is made. Factors or events that could cause our actual results to differ may emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for us to predict all of them. We do not plan to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements except as required by law.
The views expressed in this material do not necessarily reflect those of the Green Blockchain. The information provided is solely for educational purposes and should not be considered as financial advice. We strongly encourage individuals to conduct their own research and exercise independent judgment before making any financial decisions. We hold no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided.

